Explain How Differences in Air Pressure Influence Wind
Explain how the transfer of heat changes in air pressure and differences in air masses create weather wind. Changes in air pressure are determined by a variety of forces including the density and temperature of air masses.
A good example is how tropical depression forms where warm air over hot tropical waters rise and high-pressure.

. When the wind slows the Coriolis Effect is lessened. Air masses occur or originated over oceans water it contain high humidity and produce moist weather. Movement of air masses Air masses sit over the source of region or it migrate passes over new landscapes.
Radiation from the sun heats the air unevenly in different areas above earths surface causing air masses to have different temperatures and humidity levels. Squalls are strong winds of. Cold air is denser and creates greater air pressure and so it will sink.
Weather Events Caused by Air Pressure Where a high pressure and low-pressure areas meet are called fronts. Fast blowing winds originate due to the difference between air pressures at earth surface but on the other hand air pressure decreases as the height increases in spite of this we do not. As air rises the pressure lowers and surrounding air moves in to replace it causing wind.
Air pressure and height are reversely proportional to each other which means air pressure decreases due to increase in height. As the number of molecules increases they exert more pressure on a surface and the total atmospheric pressure increases. Wind is caused by differences of pressure in the Earths atmosphere.
On Earth the main differences in air pressure are caused by differences in temperature. In the Northern Hemisphere if you put your left hand to the low pressure the wind will be blowing at your back. It is dry and hot.
Although these two physical variables may at first glance appear to be quite different they are in fact closely related. When warm air rises cooler air will often move in to replace it so wind often moves from areas where its colder to areas where its warmer. The pressure difference between two locations is called a pressure gradient and the force that actually moves air as wind is called the pressure gradient force.
The colder months see more low-pressure zones as the colder air tends to weigh more creating more pressure near the surface than above which produces more unstable weather patterns such as rain snow ice and wind. The hot air rises and creates an area of low pressure on the land. The greater the pressure difference between the pressure zones the faster the wind moves.
Wind exists because of horizontal and vertical differences gradients in pressure yielding a correspondence that often makes it possible to use the pressure distribution as an alternative representation of atmospheric motions. Pressure Gradient Force PGF - causes horizontal pressure differences and winds 2. It is at these fronts that more.
The wind is caused by differences in atmospheric pressure which is mainly caused by temperature difference. At sea the difference in air temperature does not change very much between day and night whereas on land there will be a large difference. But the rate of fall in air pressure decreases with increase in height.
On a rotating planet air will also be deflected by the Coriolis effect except exactly on the equator. The differences in air density causes wind which results in horizontal differences in air pressure. The number of air molecules above a surface determines air pressure.
The relatively cool air flows towards the low pressure area on land. The driving force behind changes in air pressure and therefore the creation of wind is gravity. If there is a large pressure difference between two points that are far away the wind speeds will be lower than if those locations are closer together.
The wind is a result of forces acting on the atmosphere. Air from a high pressure area will move towards an area of low pressure. Anywhere and each time there are differences in atmospheric air pressure there will be wind because air will move from the high-pressure area to the low-pressure area.
When a difference in atmospheric pressure exists air moves from the higher to the lower pressure area resulting in winds of various speeds. Convection in the atmosphere creates the planets weather. High winds are caused when air moves between areas with large differences in air pressure.
Air that moves horizontally between high and low pressure zones makes wind. There are different types of winds such as gusts which are short bursts of high speed wind. The more the pressure changes over a given distance usually the faster the wind will be.
It also means that winds may be even stronger where the difference in the air pressure is greater. Since warm air is less dense and creates less air pressure it will rise. Wind is the movement of air across the earths surface.
When air moves from between areas of high pressure and low pressure wind directions and speeds may change. Wind results from a horizontal difference in air pressure and since the sun heats different parts of the Earth differently causing pressure differences the Sun is the driving force for most winds. Continental air masses c The air masses found over the land known as continental air masses.
These pressure systems are both the result and the cause of atmospheric circulation. Wind is defined as the sustained horizontal movement of air and is caused by changes in air pressure. This is called pressure gradient force.
However in aviation its measured in knots kt 1kt 115mph. This causes the wind to slow down. The ocean however heats slower.
The next thing that effects direction is surface friction. To other influences to explain the changes in wind. This causes the wind near the surface of the Earth to turn back toward the original high to low pressure.
When you watch the weather forecast on TV youll see the wind measured in mph. By contrast if the number of molecules.

Icse Solutions For Class 9 Geography Atmospheric Pressure And Winds A Plus Topper Atmosphericpressurebelts Geography Pressure Wind Names

What Is The Relationship Between Air Pressure And Wind Speed In A Hurricane Lisbdnet Com

Weather Unit 2 Winds And Air Pressure Science Lesson Plans Elementary Interactive Science Notebook Science Lesson Plans

Air Movement Earth Science In Maine Earth Science Upper Elementary Science Weather Science
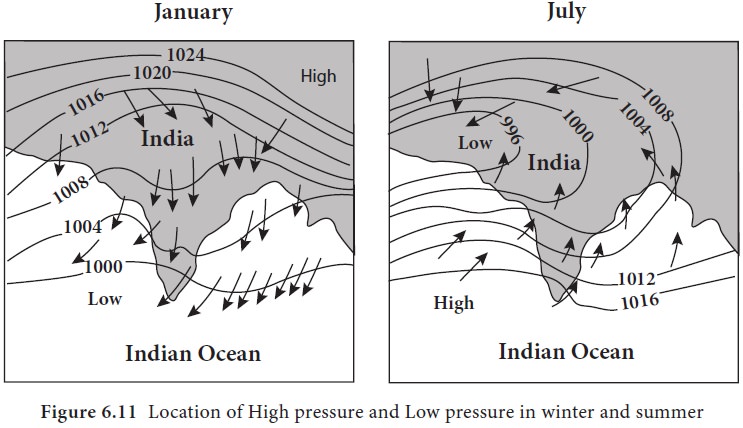
Atmospheric Pressure And Winds Geography

Wind And The Coriolis Effect Air Pressure Differences Cause The Movement Of Air Air Moving Parallel To Atmospheric Circulation Physical Geography Air Pressure
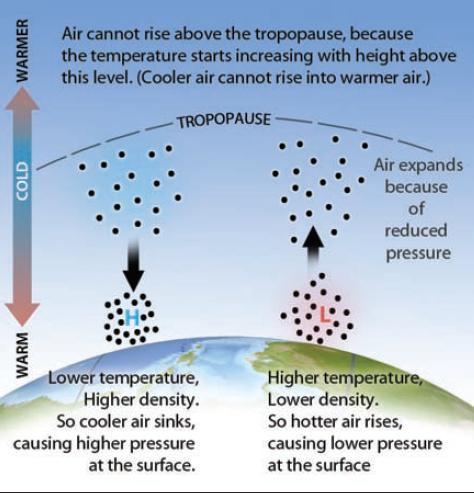
What Causes Pressure Variations And Winds
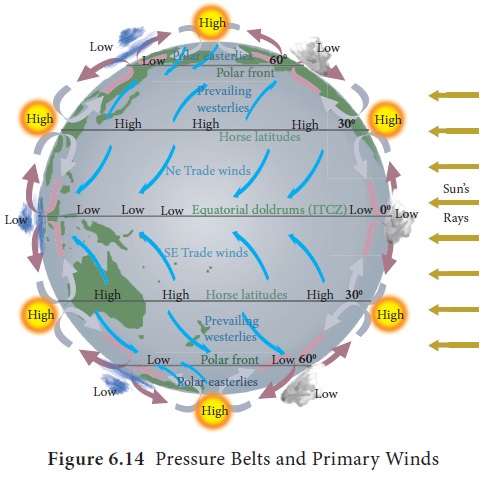
Atmospheric Pressure And Winds Geography

Atmospheric Circ Circulacion Atmosferica Atmospheric Circulation Weather Science Earth Science

The Highs And Lows Of Air Pressure Air Pressure Weather Lessons Weather And Climate

Boundaries Between Circulation Cells Air Moves Vertically Surface Winds Weak Erratic Also At Equator Whe Pattern Worksheet Atmospheric Circulation Pattern

Lesson Weather Forecasting Online Activity Interactive Weather Map Weather Map Earth Science


Comments
Post a Comment